How to Transition to a Vegan Diet: A Guide by Ottawa Healthy Meal Delivery
Over the past few years, researchers and health professionals have encouraged a shift from an omnivorous diet to a more plant-focused or vegan lifestyle, primarily for health reasons.
Vegan diets are also increasingly recognized for their ethical benefits, supporting animal welfare and reducing environmental impact. Many people are now also asking for tips on how to transition to a vegan diet in a healthy and sustainable way.
“Transitioning to a plant-based diet can be a powerful way to improve overall health while making a positive impact on the planet,” says Ronneil Ramlal, CEO of Protein Chefs. |
For these reasons, more people are exploring vegan diets and integrating plant-based meals into their daily routines.
What is a Vegan Diet?
A vegan diet excludes all animal products, including meat, dairy, eggs, fish, and sometimes honey. Instead, it focuses on plant-based foods such as:
Fruits and vegetables
Legumes (beans, lentils, peas)
Whole grains
Nuts and seeds
Common vegan substitutes include plant-based milks (soy, oat, almond), tofu, tempeh, legumes, and meat alternatives like seitan or plant-based burgers.
For those considering a vegan diet transformation, the shift can be both healthy and budget-friendly.
In fact, studies show that vegetarian and vegan diets are among the most affordable eating patterns, reducing food costs by up to 34% compared to meat-based diets. This makes plant-based eating not only good for your body and the planet, but also great for your wallet.
Health Benefits of a Vegan Diet by Ottawa Healthy Meal Delivery
Switching to a vegan diet overnight can feel restrictive and may increase the risk of nutrient gaps. Learning how to become a vegan slowly allows you to:
Reduce dietary shock and improve adherence
Learn to enjoy plant-based foods gradually
Experiment with substitutes and meal planning
Adjust social habits without feeling deprived
Studies show that those who transition slowly tend to maintain their new eating patterns longer than those who go "all or nothing."
Start Your Plant-Based Journey Today
Explore Protein Chefs’ meal options to make vegan eating stress-free and enjoyable.
Step-by-Step Guide to Planning Your Vegan Transition
Transitioning to a vegan diet becomes much easier when approached gradually and intentionally. The key is creating a plan that fits your lifestyle and allows for small, achievable changes over time.
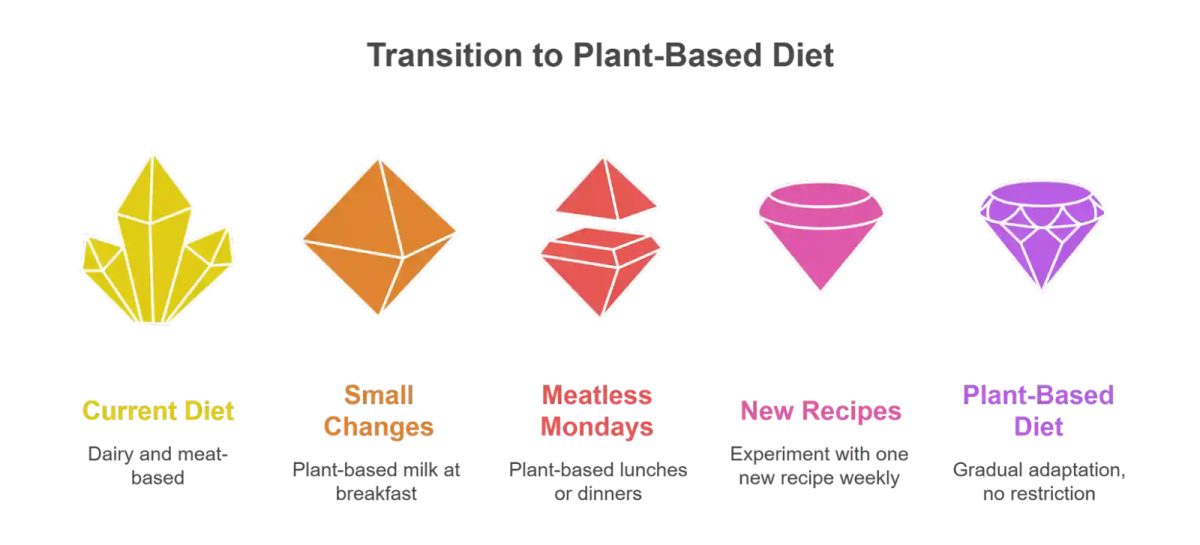
1. Set Realistic Goals
Start by introducing small, manageable changes:
Replace dairy with plant-based milk at breakfast.
Try “Meatless Mondays” as your first step toward plant-based lunches or dinners.
Experiment with one new plant-based recipe each week.
By focusing on gradual changes, you give your body and taste buds time to adapt without feeling restricted.
2. Focus on One Meal or Food Group at a Time
It’s easier to swap meals incrementally rather than overhaul your entire diet at once. For example:
Breakfast: Swap cow’s milk for soy or oat milk, or try a tofu scramble instead of eggs.
Lunch/Dinner: Experiment with lentil or bean-based dishes, plant-based burgers, or vegetable stir-fries.
Once you feel comfortable with one meal, expand your swaps to other meals throughout the day.
3. Stock a Vegan-Friendly Pantry
Having the right staples on hand makes preparing plant-based meals simple and stress-free. Essentials include:
Proteins: Beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh
Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, whole-wheat pasta
Nuts & Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds, pumpkin seeds
Vegetables & Fruits: Fresh or frozen for convenience
Other: Plant-based milks, sauces, and condiments
Meal prepping and planning ahead can save time, reduce stress, and help you maintain a balanced diet.
4. Embrace Flexibility
Transitioning to a plant based diet is a journey, not a race. Allow yourself occasional slip-ups without guilt, and focus on progress, not perfection. Over time, plant-based meals will naturally become part of your routine, and you’ll discover new favorite foods along the way.
How to Stay Nutritionally Balanced on a Vegan Diet
A vegan diet can be very healthy, but it requires some planning to ensure you get enough protein, vitamin B12, iron, calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3s.
Vitamin B12: B12 occurs naturally only in animal products. Plant-based foods do not contain it on their own, so vegans need to get B12 from fortified foods, such as plant-based milks, cereals, and nutritional yeast or from supplements.
Adequate B12 intake is essential, as deficiency can lead to anemia and nerve damage. Always check labels for B12 content and consider a reliable supplement.
Iron: Plant iron (non-heme) is absorbed less efficiently; pairing beans, lentils, and leafy greens with vitamin C-rich foods (like citrus or bell peppers) helps enhance absorption. However, for populations such as women of childbearing age, vitamin C alone may not provide enough iron due to the low bioavailability of plant iron.
Iron-fortified cereals offer a more bioavailable source of iron and can be an important dietary option to help meet iron needs more effectively.
Calcium & Vitamin D: Include leafy greens, tofu, tahini, and fortified plant milks. Vitamin D supports calcium absorption, and supplements can help when sunlight is limited.
Omega-3s: Sources include chia, flax, hemp, and walnuts. Algae-based supplements or fortified foods can help meet DHA and EPA needs.
Tip: Focus on variety and fortified foods. This keeps your diet balanced and nutrient-rich without feeling restrictive.
Managing Common Challenges When Switching to a Vegan Diet
Challenge | Tips & Solutions |
Cravings & Social Situations | Enjoy plant-based versions of favorite foods (vegan burgers, dairy-free sauces, desserts). Plan ahead for social events by eating beforehand or bringing a vegan dish. Join supportive friends or online communities. |
Eating Out or Traveling | Research menus in advance, find vegan-friendly restaurants, or carry portable snacks like nuts, hummus, or protein bars. Use apps and online tools to locate vegan options. |
Common Mistakes | Avoid relying too heavily on processed vegan foods, neglecting nutrients, or transitioning too quickly. Set realistic goals and pace yourself to create lasting habits. |
Helpful Tools, Recipes, and Resources for Beginners
Transitioning to a vegan diet is easier when you have the right tools and resources:
Meal Planning Apps: Track nutrients, plan grocery lists, and explore new recipes.
Vegan Guides & Communities: Access beginner guides, recipe collections, and online support groups.
Pantry Staples: Stock up on beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and frozen vegetables.
Products & Meal Plans: Tools like Protein Chefs’ products simplify protein intake and meal prep.
By leveraging these tools, you can reduce the stress of planning meals, avoid nutritional gaps, and make the transition smoother and more enjoyable.
Successfully Transition to a Vegan Diet with Protein Chefs
Transitioning to a vegan diet doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Start small, focus on nutrition, and phase in plant-based meals gradually. Track key nutrients, stock your pantry with versatile staples, and plan meals to make the transition smoother.
Flexibility is key, occasional slip-ups are normal, and support from friends, communities, or online groups can help you stay motivated.
To make the shift easier, explore Protein Chefs’ products, meal plans, and guides. With the right tools and planning, a vegan lifestyle can be healthy, enjoyable, and sustainable.



